Chapter 4 Distribution–histograms and density plots
library(tidyverse)
library(HistData)
library(ggpubr)4.1 Histograms and bin choice
Seeing the smooth and rough of data bins or binwidth, default number of bins is 30
h10.plot = ggplot(data = diamonds.df, aes(price)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 10)
h30.plot = ggplot(data = diamonds.df, aes(price)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 30)
h80.plot = ggplot(data = diamonds.df, aes(price)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 80)
ggarrange(h10.plot, h30.plot, h80.plot,
nrow=1, ncol = 3, align = "h")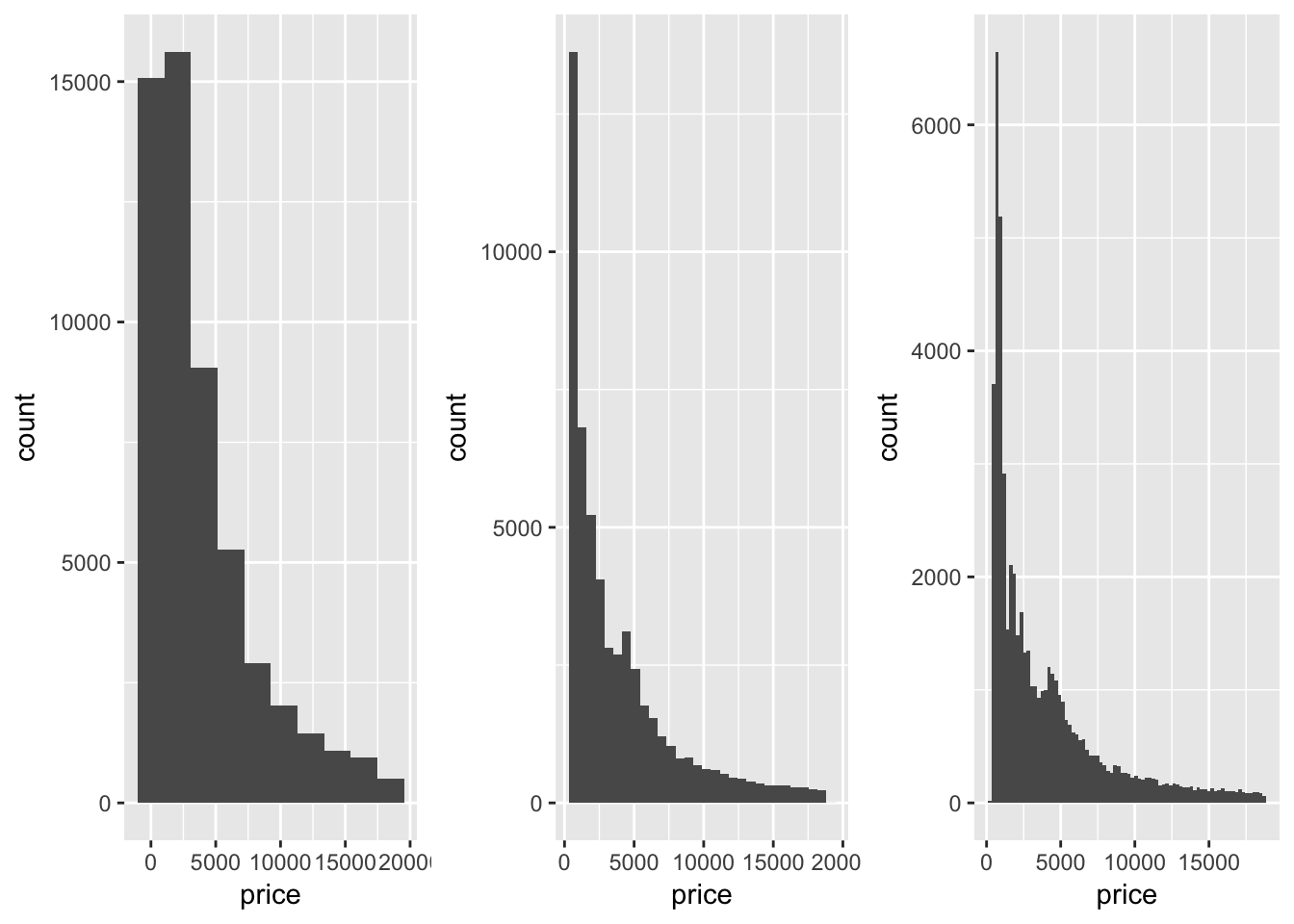
4.2 Density and kernel adjustment
Density as abstraction and model
Adjust is a multiplier on the default kernel bandwidth and so 1 represents the default
a10.plot = ggplot(data = diamonds.df, aes(price)) +
geom_density(adjust = 10)
a1.plot = ggplot(data = diamonds.df, aes(price)) +
geom_density(adjust = 1)
a01.plot = ggplot(data = diamonds.df, aes(price)) +
geom_density(adjust = 0.1)
ggarrange(a10.plot, a1.plot, a01.plot,
nrow=1, ncol = 3, align = "h")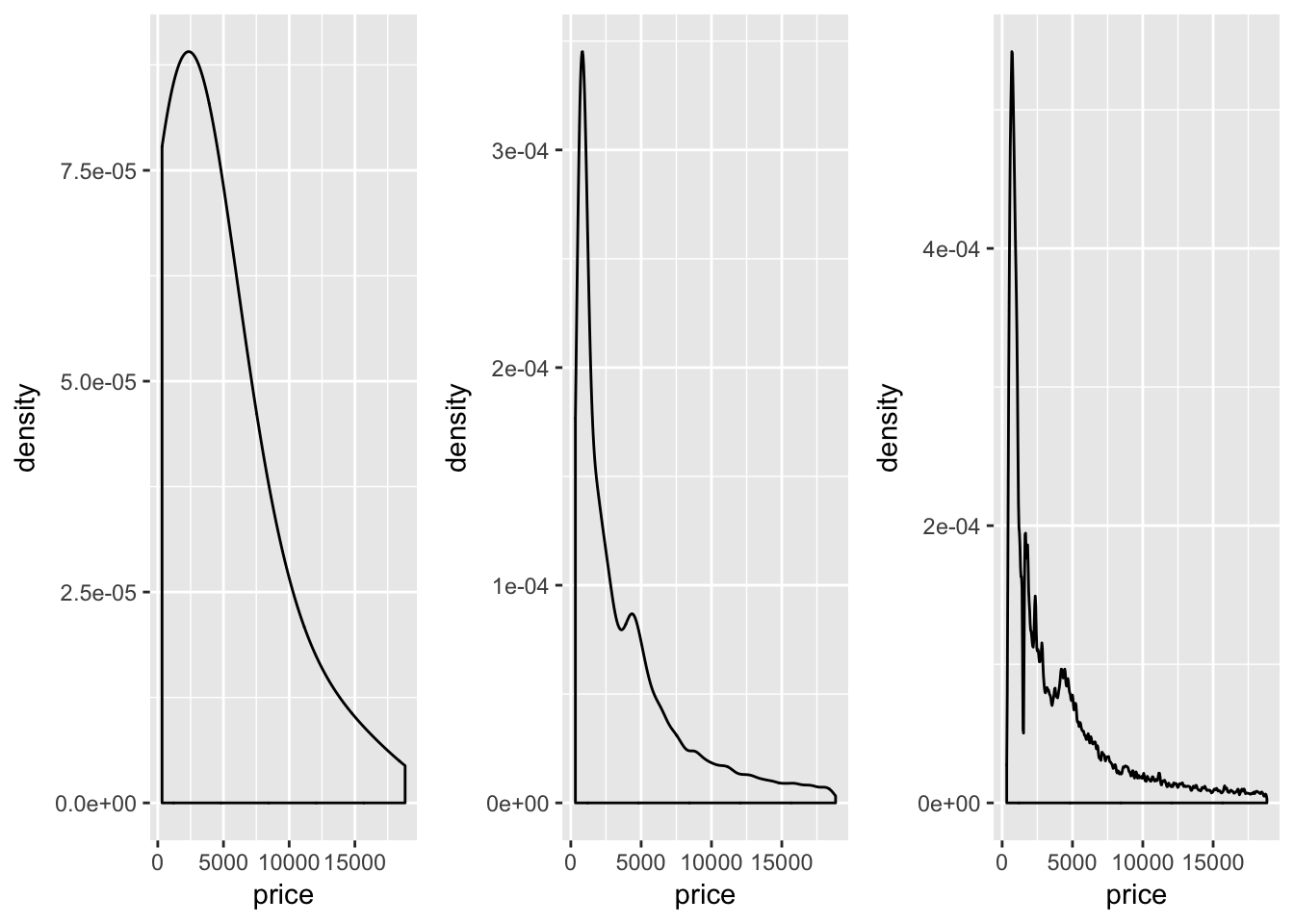
4.3 Histogram percentage rather than count
library(scales)
ggplot(mtcars.df , aes(x = as.factor(cyl))) +
geom_bar(aes(y = (..count..)/sum(..count..))) +
scale_y_continuous(labels = scales::percent)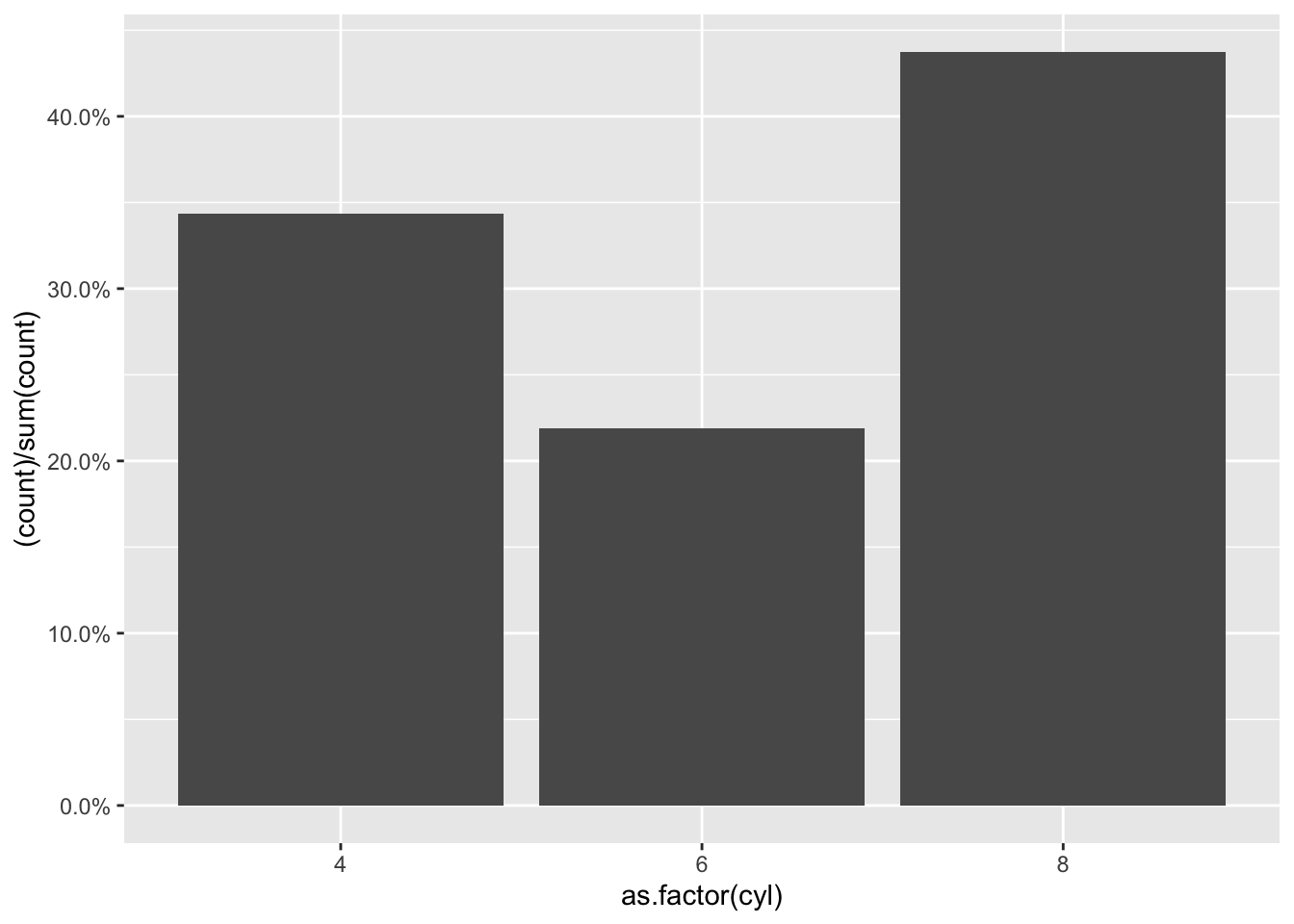
4.4 Histogram, density overlay, and normal overlay
4.5 Cummulative density
diamonds.df = diamonds
ggplot(diamonds.df, aes(price, colour = cut)) +
stat_ecdf(geom = "step")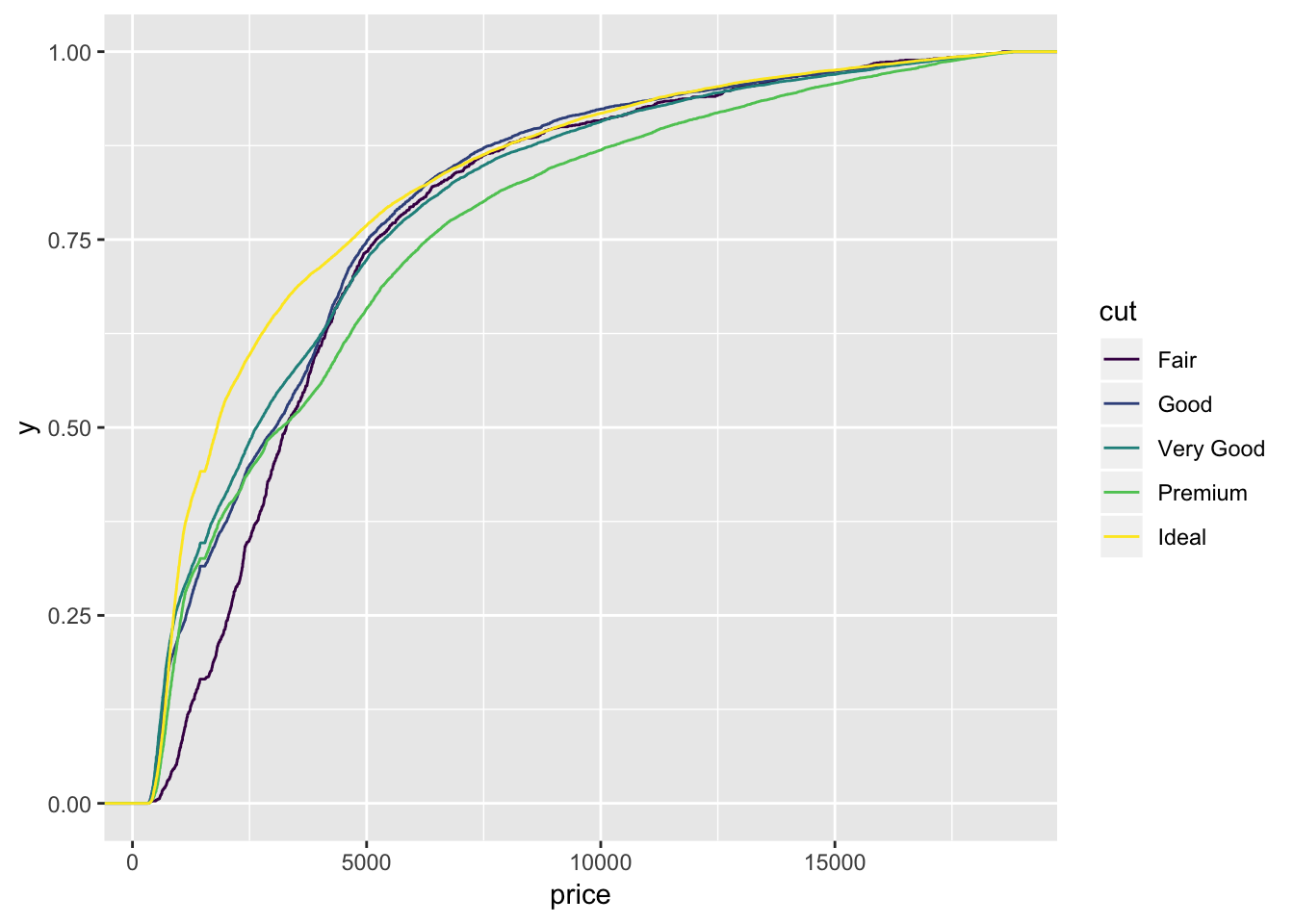
4.6 Quantile-quantle plot
Plots quantiles of sample as a function of the quantiles of the theoretical distribution.
ggplot(diamonds.df, aes(sample = price)) +
geom_qq(distribution = qlnorm) +
geom_abline(intercept = mean(diamonds.df$price), slope = sd(diamonds.df$price))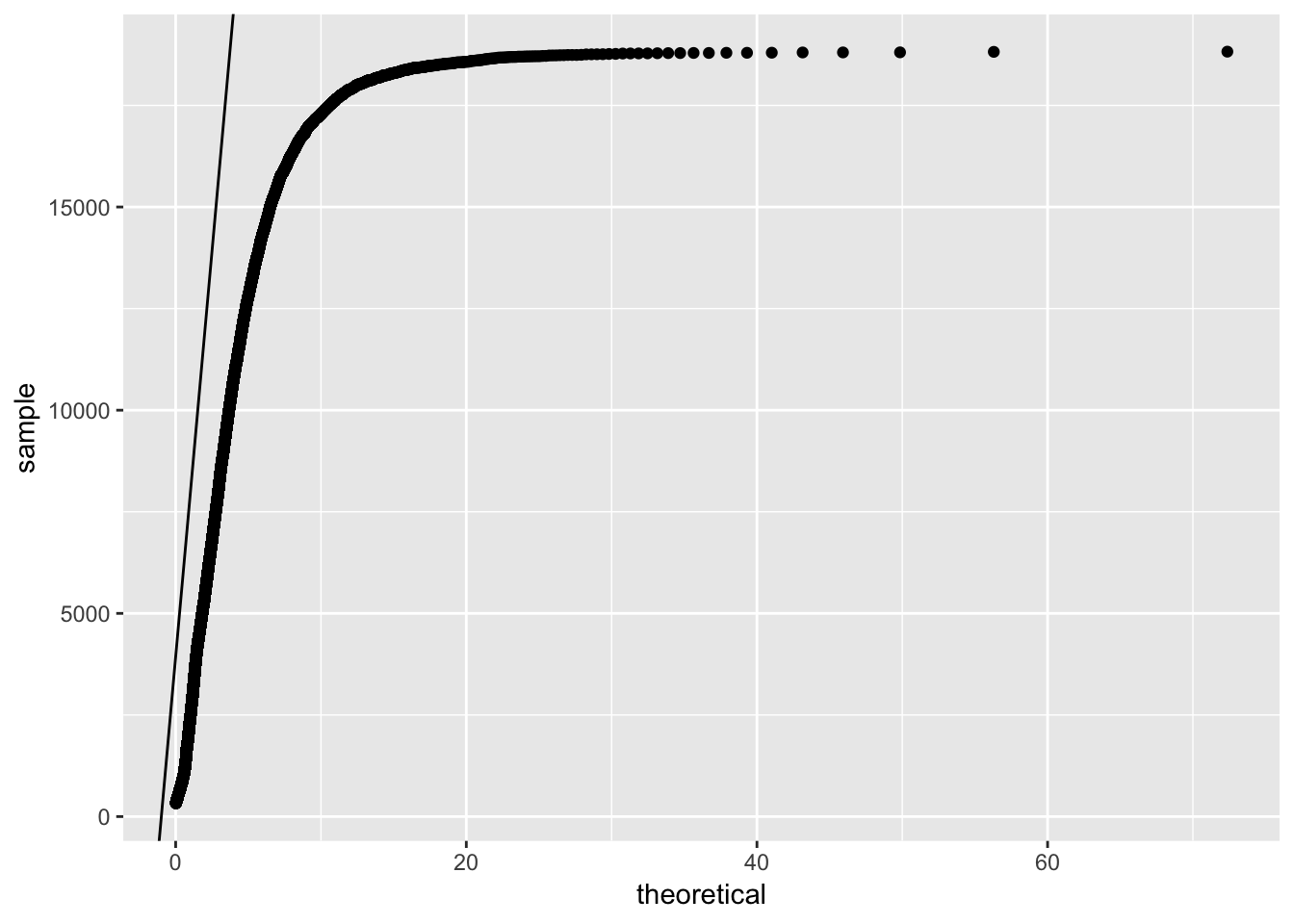
4.7 Cummulative density
ggplot(diamonds.df, aes(price, colour = cut)) +
stat_ecdf(geom = "step")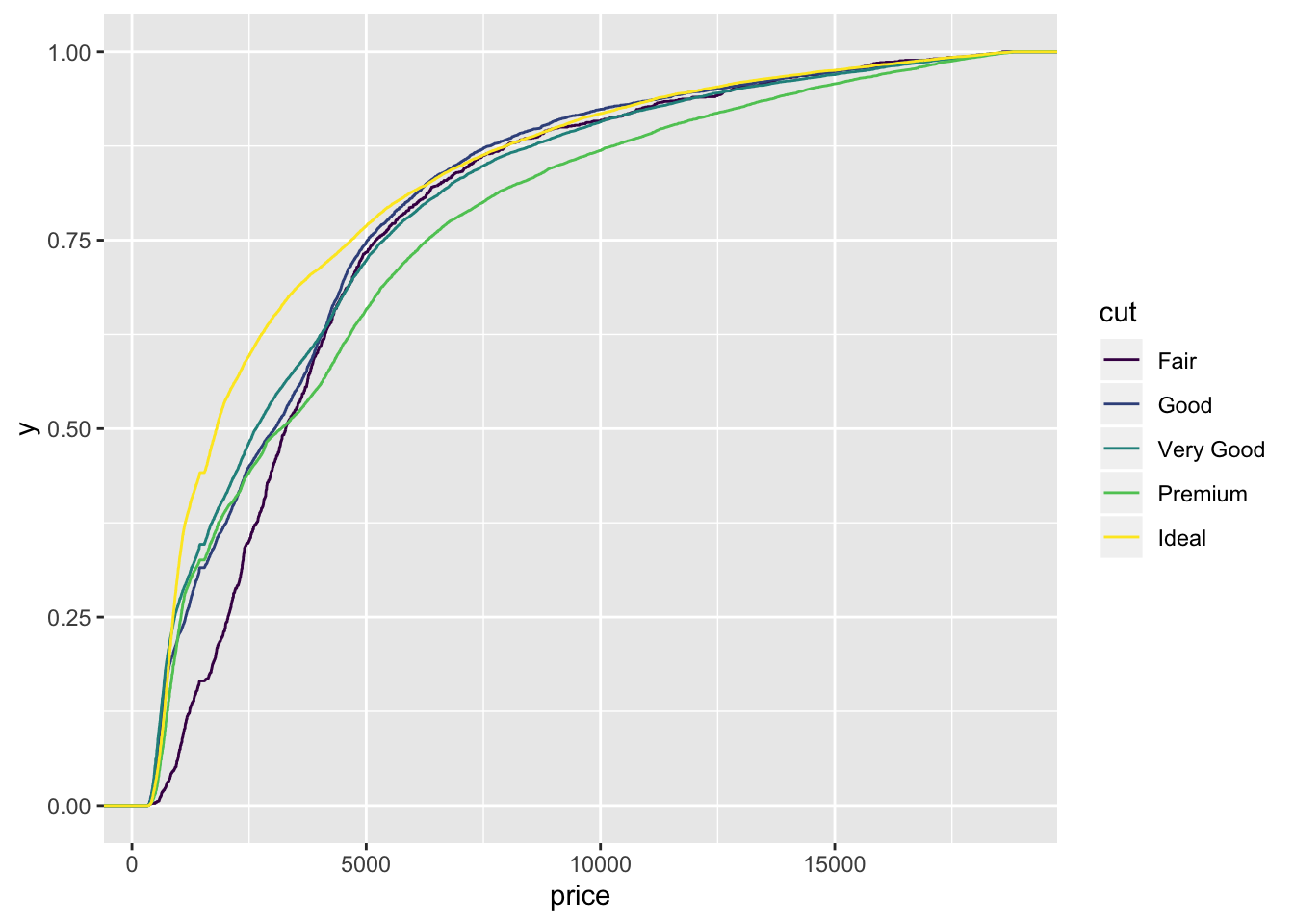
4.8 Distribution: 2-D distribution and overplotting revisited
ggplot(diamonds.df, aes(log(carat), log(price)))+
geom_point(alpha = .01)+
theme_bw()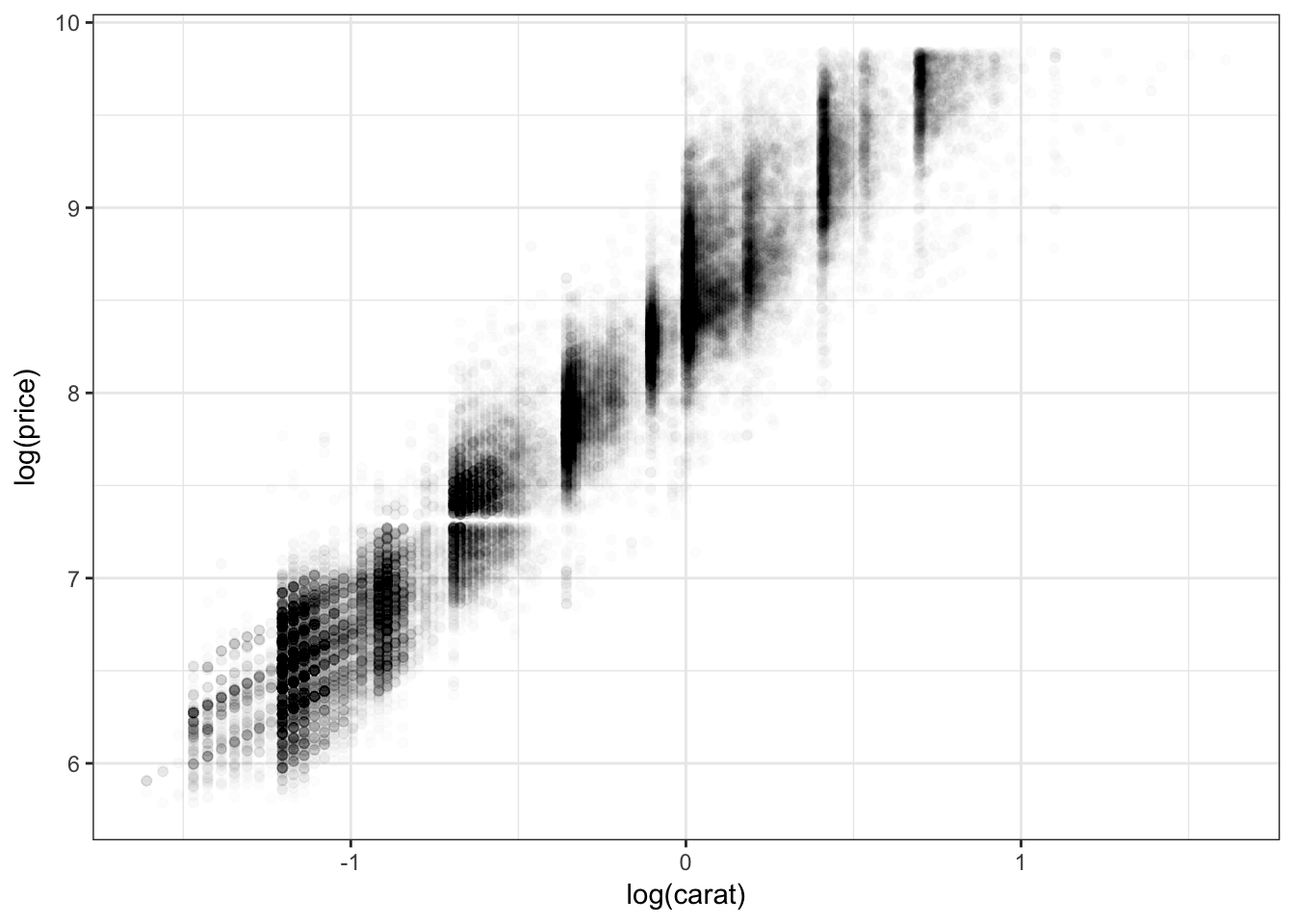
ggplot(diamonds.df, aes(log(carat), log(price)))+
geom_point(size = .5)+
geom_density2d(size=1.2)+
theme_bw()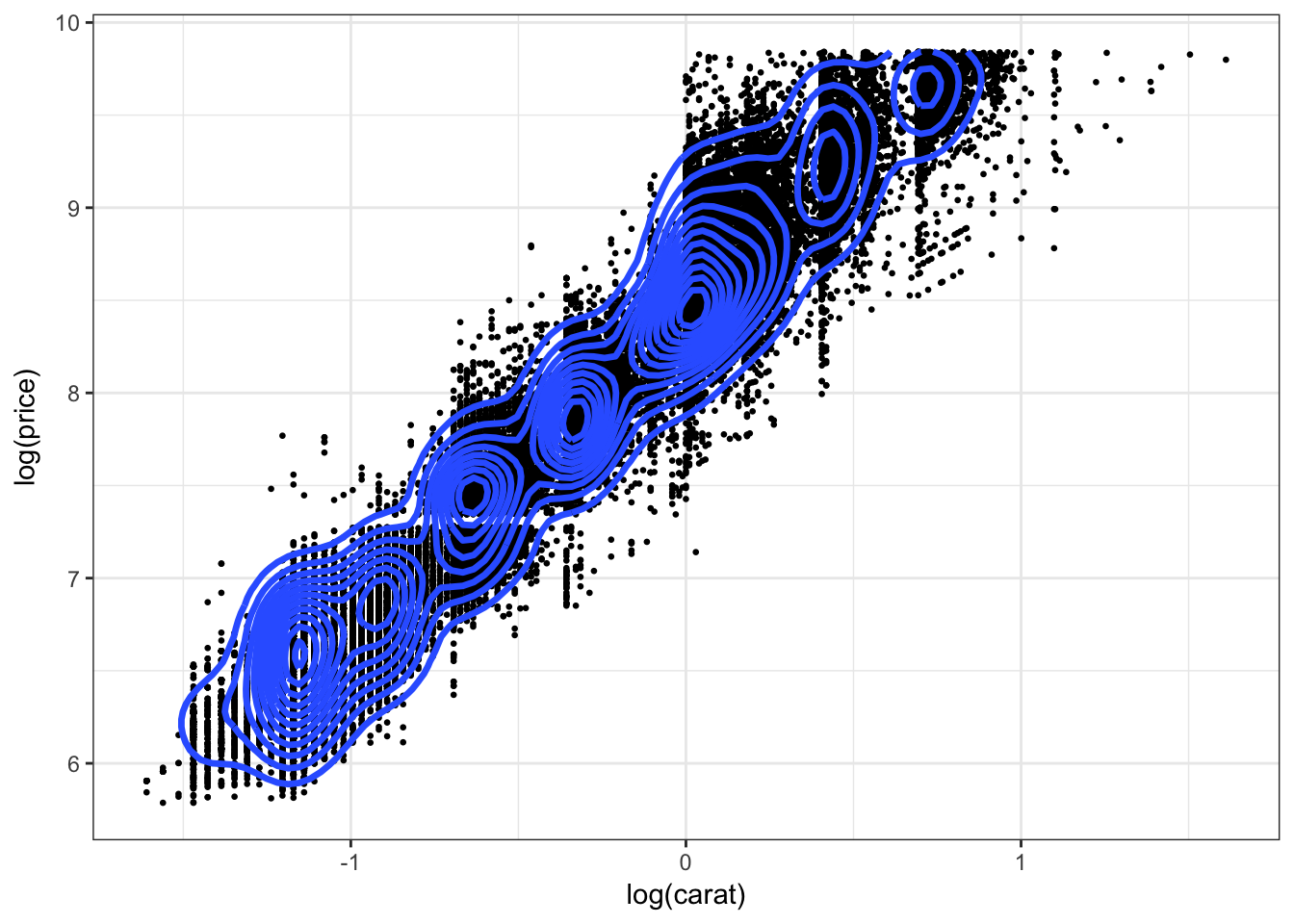
ggplot(diamonds.df, aes(log(carat), log(price)))+
geom_point(size = .5)+
geom_density2d(size=1.2)+
geom_hex(alpha = .6) +
theme_bw()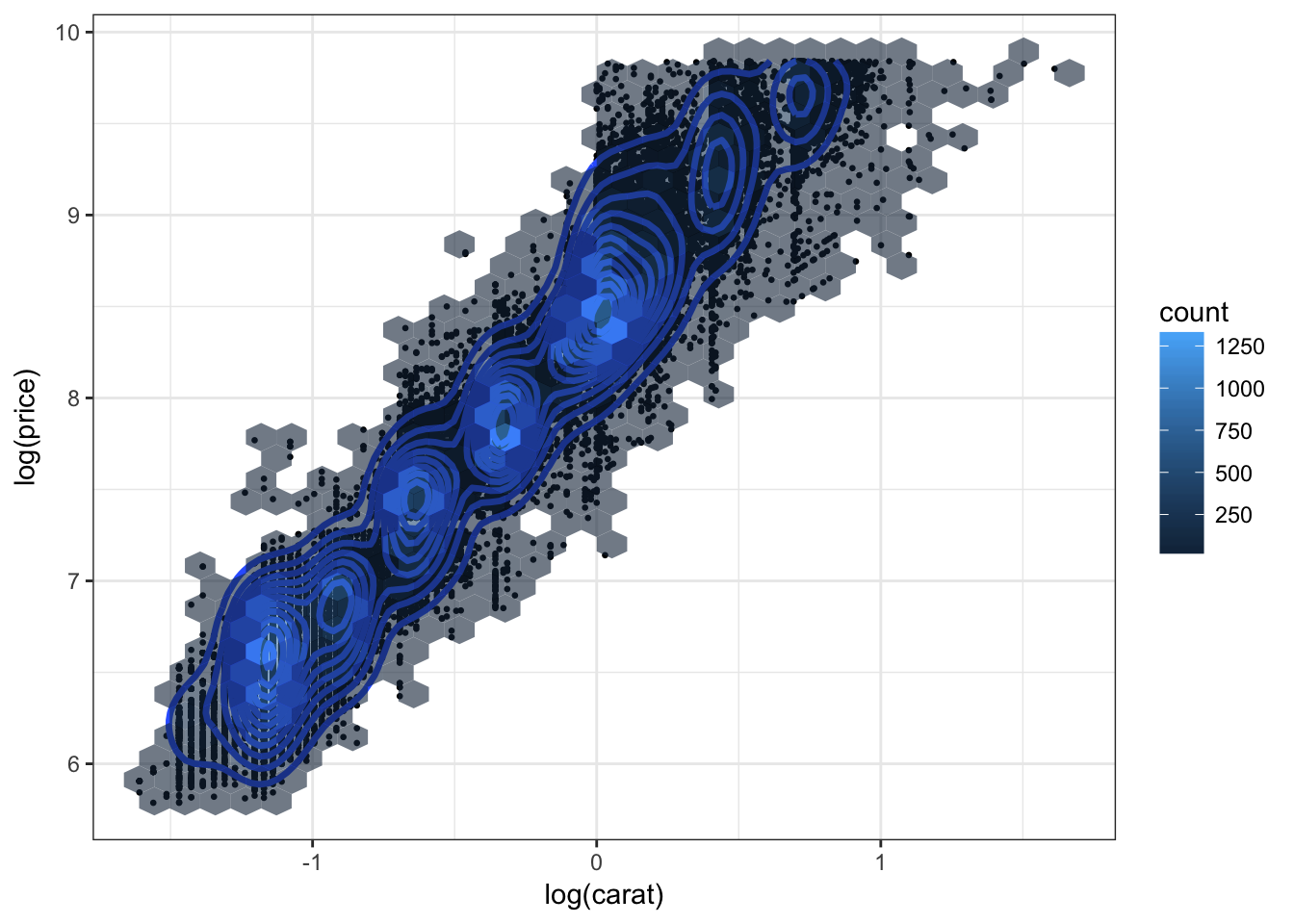
ggplot(diamonds.df, aes(log(carat), log(price)))+
#geom_point( )+
#geom_point(size = .5)+
#geom_density2d(size=1.2)+
geom_hex(bins = 50) +
theme_bw()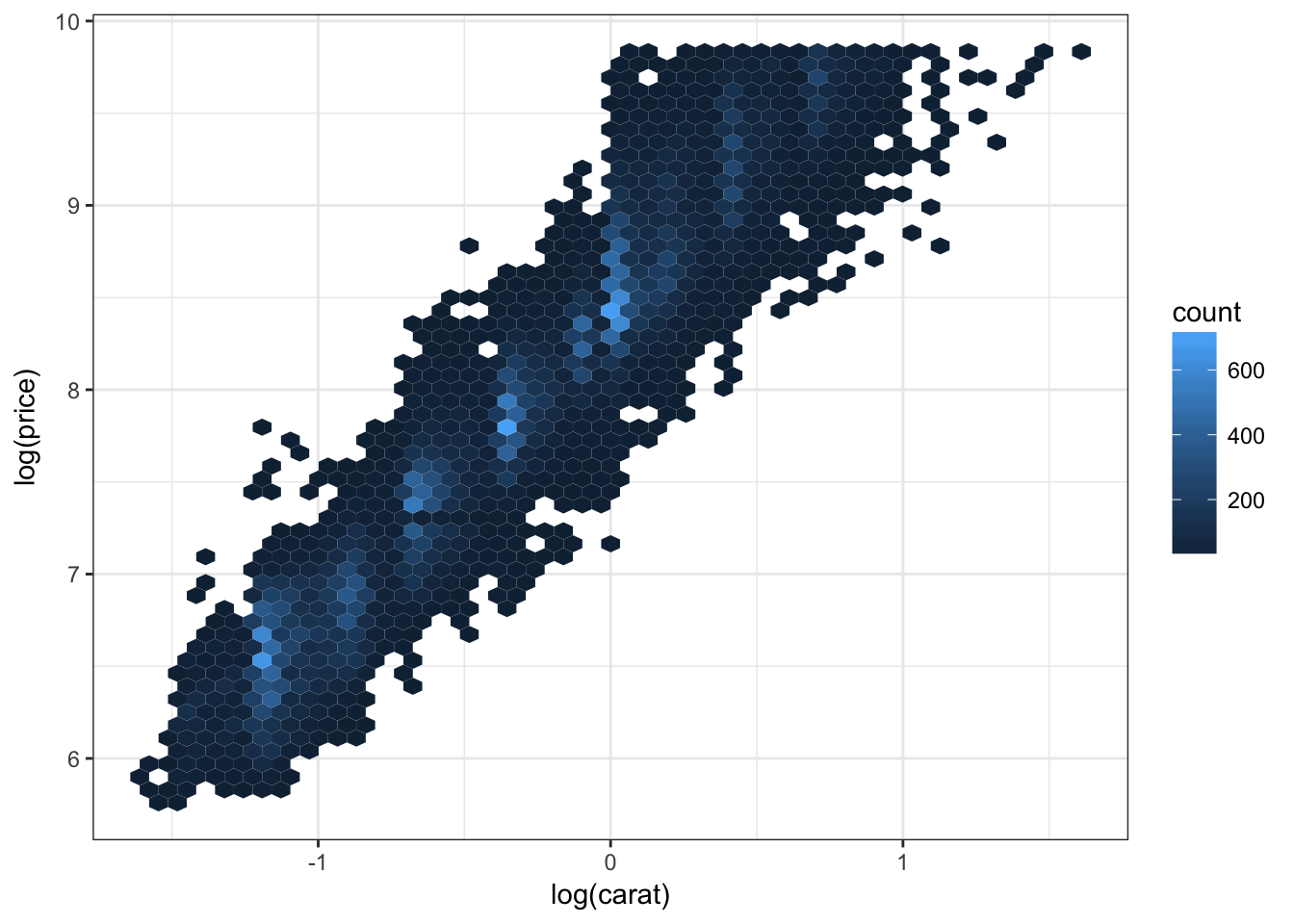
4.9 Small multiple histogram with density and median reference lines
TODO change to diversity data gender across job types
diamonds.df = diamonds
sum.diamonds.df = diamonds.df %>% group_by(cut) %>%
summarise(q85 = quantile(price, 0.85))
ggplot(data = diamonds.df, aes(price)) +
geom_histogram(aes(y = ..density..), bins = 40) +
geom_density(colour = "darkblue") +
geom_vline(data = sum.diamonds.df, aes(xintercept = q85)) +
facet_grid(cut ~ .)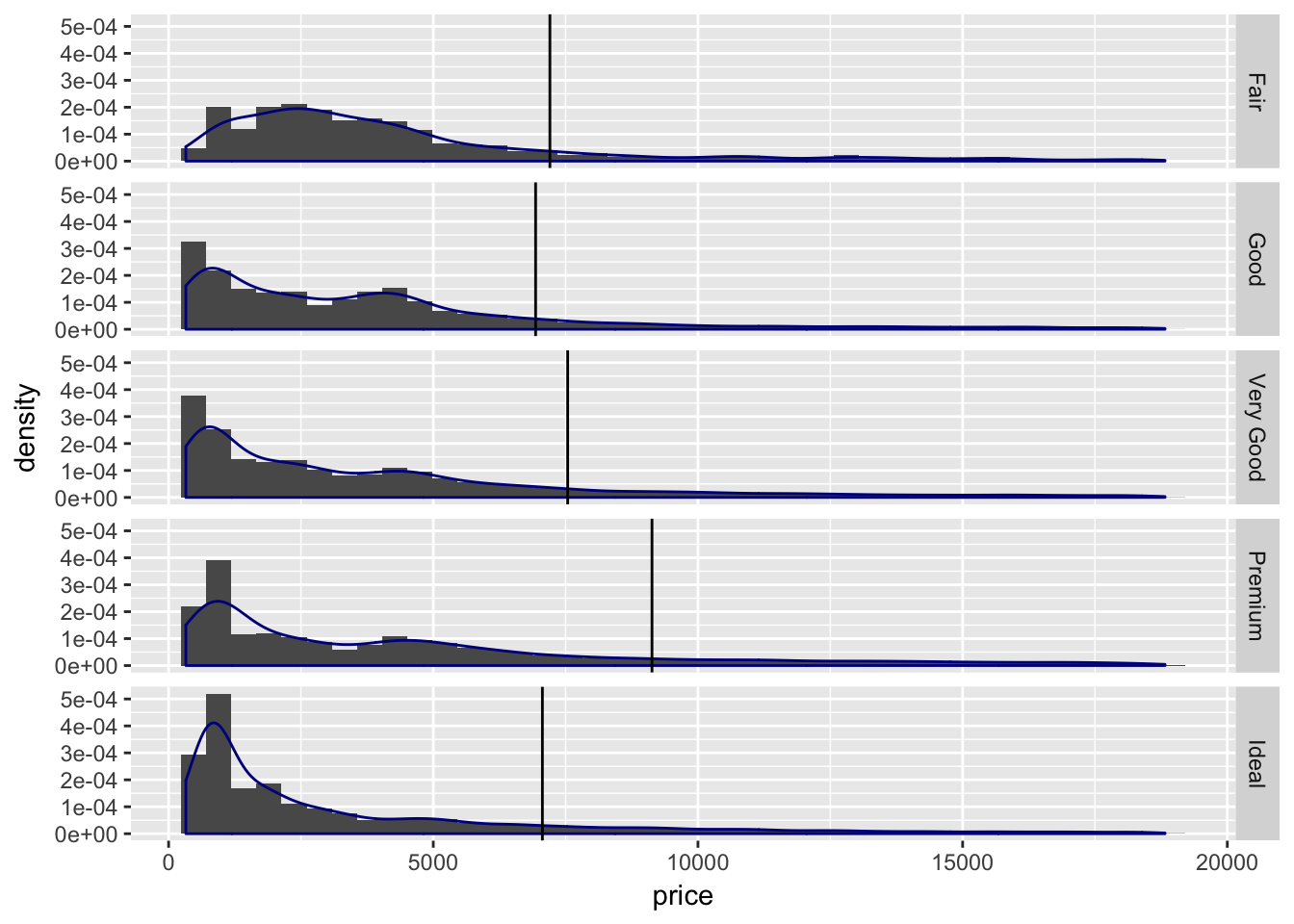
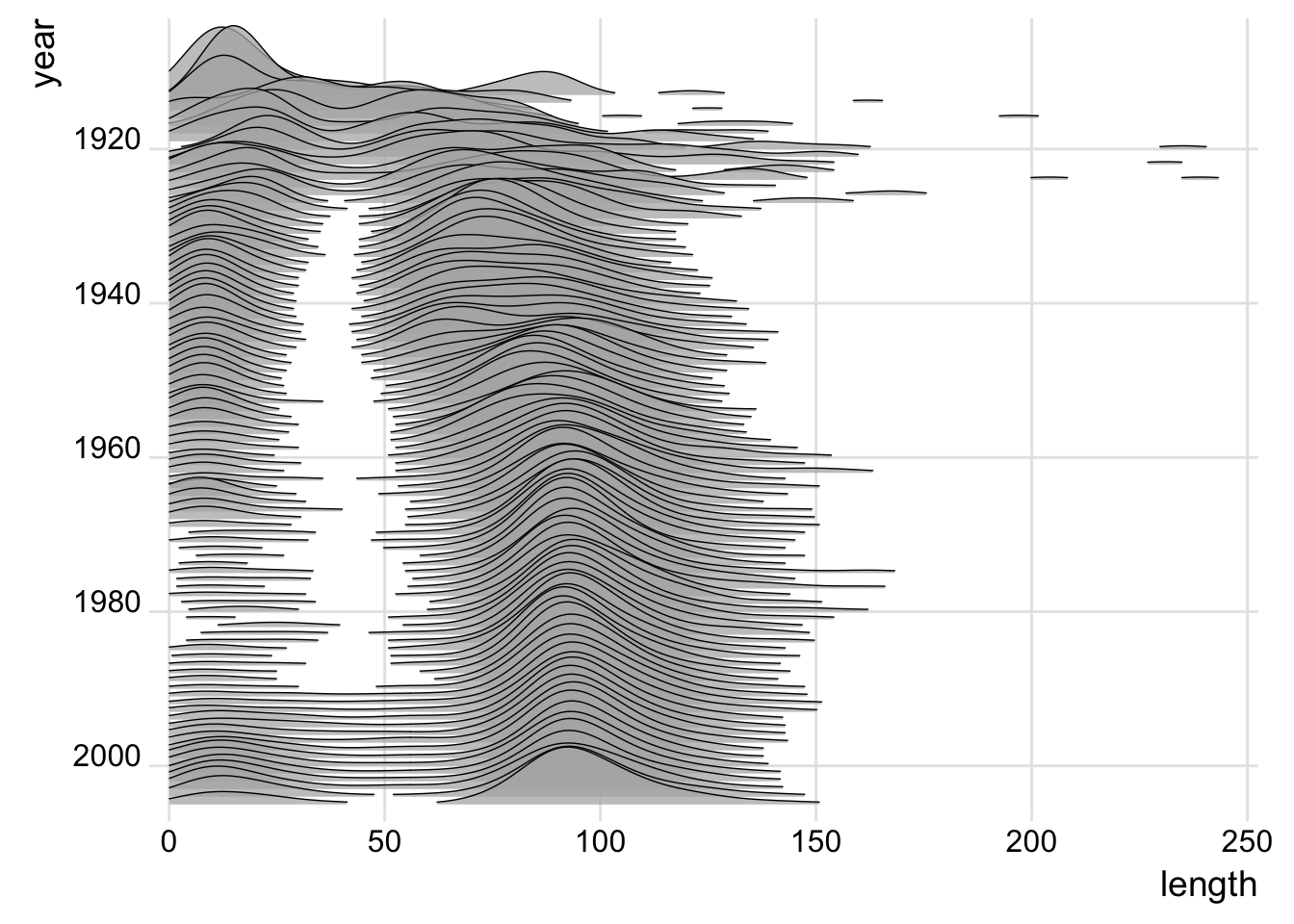
4.10 Ridge plot–An array of density plots
https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggridges/vignettes/gallery.html
library(ggridges)
library(ggplot2movies)
movies %>% filter(year>1912, length<250) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = length, y = year, group = year)) +
geom_density_ridges(scale = 10, size = 0.25, rel_min_height = 0.03, alpha=.75) +
scale_x_continuous(limits=c(0, 250), expand = c(0.01, 0)) +
scale_y_reverse(breaks=c(2000, 1980, 1960, 1940, 1920, 1900), expand = c(0.01, 0)) +
theme_ridges()## Picking joint bandwidth of 6.89